In the early hours of June 2025, the world awoke to one of the most daring aerial missions of the 21st century. The United States, in cooperation with Israel, launched a stealth airstrike targeting three of Iran’s most fortified nuclear facilities — Fordow, Natanz, and Isfahan — using B-2 Spirit stealth bombers under the codename Operation Midnight Hammer.
Washington — Senior Pentagon officials revealed new details about the U.S. operation to bomb three nuclear sites in Iran, with the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff saying it was the “largest B-2 operational strike in U.S. history” and inflicted “extremely severe damage and destruction” to the targets.
Table of Contents
Introduction: A Strike Decades in the Making
In the early hours of June 2025, the world awoke to a sudden and unprecedented show of American military precision. Dubbed “Operation Midnight Hammer,” the covert U.S. operation sent shockwaves through the Middle East, targeting critical Iranian military and nuclear infrastructure in a rapid, high-impact strike.
What appeared to be another tense standoff in the Persian Gulf region quickly escalated into a full-fledged strategic offensive — one that redefined red lines in modern warfare.
This operation wasn’t just a reactive military decision; it was the culmination of rising tensions, intelligence warnings, and geopolitical maneuvering that had been building for months. As the U.S. deployed B-2 Spirit stealth bombers, advanced drones, and cyber warfare units, the world witnessed a modern-day hammer strike — silent, swift, and deadly — executed under the veil of darkness with minimal collateral damage and maximum precision.
Operation Midnight Hammer marked a dramatic turning point in the U.S.-Iran conflict. It was not a declaration of war but a message — loud and clear — that the United States was prepared to neutralize imminent threats before they could materialize into regional chaos. Iran’s nuclear facilities, command centers, and missile sites in Fordow, Natanz, and Isfahan became primary targets, with satellite-guided munitions and electromagnetic pulse (EMP) weapons disrupting key systems without triggering a full-scale ground invasion.
As details of the operation slowly emerged from defense briefings and leaked satellite images, analysts began dissecting its implications on global diplomacy, energy markets, and regional stability. For the U.S., it was a bold reaffirmation of its strategic dominance in the region. For Iran, it was a wake-up call. And for the rest of the world, Operation Midnight Hammer became a blueprint for 21st-century warfare — one that blends conventional force with technological supremacy.
This article explores the full scope of Operation Midnight Hammer — its origins, execution, geopolitical context, and the aftermath — offering you an in-depth look into one of the most defining military operations of our time.
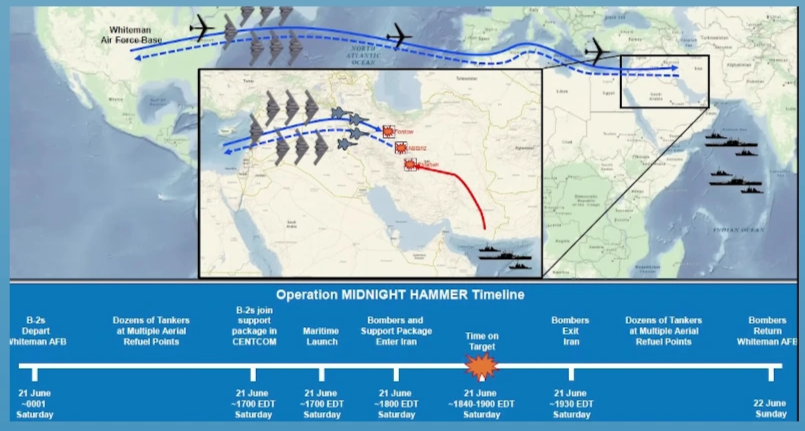
The Real Flight Path: Whiteman AFB to Tehran's Backyard
Also ready about- Operation Sindoor: How India’s S-400 Shot Down 5 Pakistani Jets and 1 AEW&C/ELINT Aircraft: IAF chief calls S-400 a ‘Game-Changer’.
The Decoy Route: An Indo-Pacific Misdirection
Pentagon Press Briefing: The Map and Message
The Pentagon stated:
Why These Three Sites?
Israel’s Role and Reaction
Iran’s Dilemma: Rage, Retaliation, or Restraint?
Source: Pete Hegseth United States Secretary of Defense
How Iran Could Block the Strait of Hormuz in Response to Operation Midnight Hammer
In the wake of the recent U.S. military action—codenamed Operation Midnight Hammer—tensions in the Persian Gulf have escalated dramatically. Iran, viewing the operation as a direct threat to its sovereignty and regional influence, has signaled that it may resort to one of its most potent forms of asymmetric retaliation: the closure or disruption of the Strait of Hormuz.
The Strait of Hormuz is one of the world’s most critical maritime chokepoints, through which roughly 20% of global oil supply passes daily. Iran, with its substantial military assets in the region—especially the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps Navy (IRGCN)—possesses both the capability and strategic incentive to obstruct this narrow waterway.
Iran’s strategy to block or threaten the strait typically involves a mix of the following:
Deployment of Fast Attack Craft and Swarm Tactics: Iran has a fleet of small, fast boats capable of executing hit-and-run attacks or laying sea mines covertly.
Mine Warfare: Iran can deploy advanced naval mines from submarines or disguised vessels to disrupt or deny access to tankers and commercial ships.
Missile Threats from the Coastline: Iran maintains anti-ship missile batteries along its southern coast, giving it the ability to target ships from land-based platforms with precision.
Use of Submarines: Iran’s fleet of mini-submarines, including the Ghadir-class, can operate in the shallow waters of the strait and pose a significant threat to commercial and naval vessels.
Hybrid Warfare: In addition to military means, Iran might use cyberattacks or proxy forces in the region to further complicate U.S. and allied operations.
By threatening to close the Strait of Hormuz, Iran is not only responding to Operation Midnight Hammer, but also leveraging its geographic advantage to exert global economic pressure, especially on oil-importing nations. This form of strategic deterrence aims to force a recalibration of U.S. policy in the Gulf and to raise the costs of continued military confrontation.
In essence, the strait becomes both a symbolic and literal pressure point—where Iran’s asymmetric warfare doctrine converges with its geopolitical interests in the face of escalating U.S. operations.
Author’s Viewpoint
The strike known as Operation Midnight Hammer was more than a military raid — it was a strategic signal, by targeting Iran’s critical nuclear-sites at Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan under Operation Midnight Hammer with US B-2 bombers and deep-penetrating munitions, the United States demonstrated not just capability but willingness to act pre-emptively.
In my viewpoint – The U.S. choice to strike reflects a belief that Iran’s nuclear programme had crossed a threshold where waiting or negotiating alone was no longer viable. At the same time, it accepted the risk of escalation: by entering Iran’s territory so forcefully, the U.S. placed itself in a more exposed position.
The viewpoint emphasizes that the operation served both as a physical blow and psychological message — to Iran, the region, and the world: “We can reach you, deeply hidden as your assets may be.” But also to have a key attention on these angles : destroying infrastructure is one thing; controlling the aftermath, preventing retaliation and managing regional consequences is another.
While Iran’s sites were hit hard, I believes that the long-term success will depend on whether the operation forces Iran back to negotiation or merely provokes deeper entrenchment.
Strategic Implications: A New Middle East Doctrine
Strategic Geography and Iran’s Leverage
The Strait of Hormuz is a narrow maritime passage, just 21 nautical miles wide at its narrowest point, with designated shipping lanes only 2 miles wide in each direction. Iran controls the northern coastline of the strait and maintains strategic positions on the islands of Qeshm, Hengam, and Abu Musa. This gives Iran the geographical upper hand to monitor and rapidly deploy naval or aerial assets in the area.
Political Signaling and Deterrence
Iran doesn’t necessarily need to close the strait completely to make its point or extract concessions. Limited harassment, symbolic strikes, or a temporary shutdown through mining could serve as coercive diplomacy—sending a signal to both Washington and global markets. The mere suggestion of a possible blockade often causes oil prices to spike, amplifying Iran’s leverage without actual engagement.
Lessons for India
- when an adversary reaches a point of near-irreversible capability (as Iran did), delaying action may reduce options. India must monitor adversaries (state or proxy) and recognise when thresholds are approaching.
- Build visible deep-strike credibility. The U.S. used specialised platforms and weapons to reach underground sites at Iran. India must ensure its own deterrent includes not only defence but strike-depth, signalling the ability to act if required.
- Don’t underestimate escalation risks. Striking another state’s key infrastructure invites blowback — military, diplomatic, regional. India must prepare for second-order effects: proxy attacks, maritime disruptions, supply-chain shocks.
- Maintain regional strategic flexibility. The strike shows that global powers may act with little regional consultation. India must retain the autonomy to respond to sudden shifts and ensure its defence posture and diplomacy are robust enough to adjust.
- Hardening isn’t enough — deployment and mobility matter. The Iran sites were deeply buried and fortified. The author suggests that simply hiding or hardening assets may not suffice when the enemy has specialised weapons. Indian strategic assets must be dispersed, resilient, and backed by intelligence.
- Geopolitical ripple-effects will hit beyond the strike zone. Although the operation targeted Iran, its aftershocks will affect the Persian Gulf, energy flows, alliances, non-proliferation regimes. India’s strategic calculus must include these wider impacts: oil import security, regional stability, supply-chain diversification.
Conclusion: A Hammer in the Night, A Message in the Day
FAQ – Operation Midnight Hammer: US Strike on Iran’s Nuclear Sites
- What was “Operation Midnight Hammer”?
Operation Midnight Hammer refers to the coordinated strike by U.S. forces on Iran’s underground nuclear facilities—aimed at disrupting Iran’s nuclear-weapons progress. - Which Iranian nuclear sites were targeted?
The operation focused on deeply buried facilities at locations such as Natanz, Fordow and the Isfahan uranium-conversion site, as part of the U.S. mission to degrade Iran’s breakout potential. - Why did the U.S. decide to act now?
The U.S. assessed that Iran was approaching a threshold where a nuclear breakout could become irreversible. The strike was deemed necessary to preserve U.S. strategic options and deter further escalation. - What are the immediate risks following the strike?
The major risks include Iran retaliating via proxies (in Iraq, Syria, or the Gulf), missile/drone attacks, disruption of shipping lanes (such as the Strait of Hormuz), and broader regional destabilisation. - Does this operation end Iran’s nuclear ambitions?
No. While it severely sets back aspects of Iran’s infrastructure and signals a strong deterrent, Iran still retains the knowledge, personnel and network to rebuild if left unchecked. The long run remains uncertain.
People Also Ask — Operation Midnight Hammer: US Strike on Iran’s Nuclear Sites
- How will Operation Midnight Hammer affect U.S.–Iran relations in the coming years?
This operation pushes U.S.–Iran relations into a more direct confrontation phase. Trust is already zero, and now Iran will see every negotiation offer as a pressure tactic. The U.S. will tighten sanctions and military presence, while Iran is likely to strengthen proxy networks and accelerate hidden nuclear work. Expect a long period of tension with no easy diplomacy. - What role does Israel play after the U.S. bombed Iran’s nuclear sites?
Israel benefits the most from this strike. It has always considered Iran’s nuclear programme an existential threat. After the U.S. attack, Israel will push for continued military pressure so Iran cannot rebuild. It may support the U.S. with intelligence and possibly conduct its own covert operations against Iran’s scientists and missile sites. - Could this strike trigger a full-scale war in the Middle East?
Yes, the risk is real — but not immediate. Iran doesn’t want direct war with the U.S., so it will likely retaliate indirectly through militia attacks, drones, cyber warfare, and maritime disruption. If any side miscalculates — especially involving Israel — the situation can escalate into a regional conflict very fast. - What should India’s defence and foreign policy take-away be from the U.S. strike on Iran?
India must prepare for three things:
1. Energy security — because instability in the Gulf threatens oil supplies.
2. Deep-strike capability — India needs strong long-range platforms like the U.S. used.
3. Diplomatic balance — India must maintain ties with both the U.S. and Iran to protect trade, diaspora and security interests. - Will other countries now try similar deep-strike attacks on nuclear infrastructure following this precedent?
Possibly. This strike shows that hardened underground bunkers are not untouchable. Countries with strong air-power might feel more confident using pre-emptive strikes if they believe negotiations will fail. On the other side, nations working on nuclear programmes may hide deeper or disperse facilities faster to avoid similar attacks.
Types of Missiles in India: Indian Missile Systems.

Pratik Kondawale
Strategist | Indian Defence & Global Affairs
Founder of GeoLens.in, Pratik writes in-depth analysis on India’s defence strategy, military tech, and global power shifts delivering sharp insights through an Indian lens.

“Will shoot first, ask questions later.” Why Trump wants Greenland and why it is so important ? In 2026
Why Trump wants Greenland and why it is so important goes far beyond a controversial proposal or diplomatic provocation. Greenland sits at the center of a rapidly militarizing Arctic, rich in critical minerals, emerging sea routes, and strategic military value.
Trump’s interest reflects deeper U.S. concerns over national security, Russian and Chinese Arctic expansion, and long-term control over resources that underpin global economic power. Denmark’s unusually harsh military warning shows this is not political theater but a genuine sovereignty crisis. As climate change unlocks Arctic access, Greenland has become a frontline in great-power rivalry, where a single miscalculation could fracture NATO, destabilize global markets, and reshape the world order.

Operation Absolute Resolve: How the U.S. Capture of Nicolás Maduro Reshaped Global Geopolitics
Operation Absolute Resolve marks one of the most controversial U.S. military actions in recent history. In January 2026, American forces reportedly captured Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro and transferred him to U.S. custody, triggering global shock and debate. Officially justified by national security, narco-terrorism, and migration concerns, the operation is widely seen by analysts as driven by deeper geopolitical motives—especially Venezuela’s vast oil reserves and its alignment with U.S. rivals. This article examines how Operation Absolute Resolve unfolded, the legal and strategic risks it poses, global reactions, and what the crisis means for India and the future of international order.

India Is Surrounded by Unstable Neighbours — What are the Real Challenges and Opportunities Does This Create?
India Is Surrounded by Unstable Neighbours, a reality that is steadily shaping its strategic environment. Political turmoil, economic collapse, military dominance, and external interference across South Asia create constant pressure on India’s borders and internal security. Yet, this instability also forces New Delhi to adapt—by strengthening defence preparedness, expanding diplomatic influence, securing trade routes, and positioning itself as a stabilizing power in the region. This article examines the real challenges India faces and the strategic opportunities emerging from a volatile neighbourhood.

Tejas Crash at Dubai Air Show 2025 — A Tragedy, A Lesson, and A Call for Reform
The Tejas crash at the Dubai Air Show turned a moment of national pride into sudden heartbreak when Wing Commander Syal lost his life. This article unpacks the events of that day, explains why the Tejas crash matters for India’s defense readiness, and outlines the practical lessons and reforms needed to ensure the program recovers stronger. It also honors the pilot’s sacrifice and shows how the Tejas crash can become a catalyst for accountability, safer engineering, and faster delivery of operational jets.

Bangladesh EX-PM Sheikh Hasina Death Sentenced: Turmoil in Bangladesh and Rewired South Asian Politics
The Sheikh Hasina death sentenced verdict has detonated one of the most explosive political crises in Bangladesh’s modern history. Delivered in absentia by the International Crimes Tribunal, the ruling blames the former prime minister for orchestrating widespread state violence during the 2024 student protests. The decision has dismantled the Awami League’s long-standing dominance, pushed Bangladesh into a volatile power vacuum, and placed India in the middle of a diplomatic standoff. As questions about justice, political motivation, and regional stability collide, the fallout of this verdict is reshaping South Asian geopolitics in real time.

China with New Air Defence Near Pangong: A Silent Shift in Himalayan Power Balance
China’s new air defence near Pangong marks a major strategic escalation in the Himalayas. Satellite imagery reveals advanced HQ-9 missile systems, radar units, and fortified shelters aimed at asserting Chinese air dominance over eastern Ladakh. This development not only alters the regional military balance but also raises critical questions about India’s preparedness, response strategy, and the long-term implications for border security and geopolitical stability in South Asia.